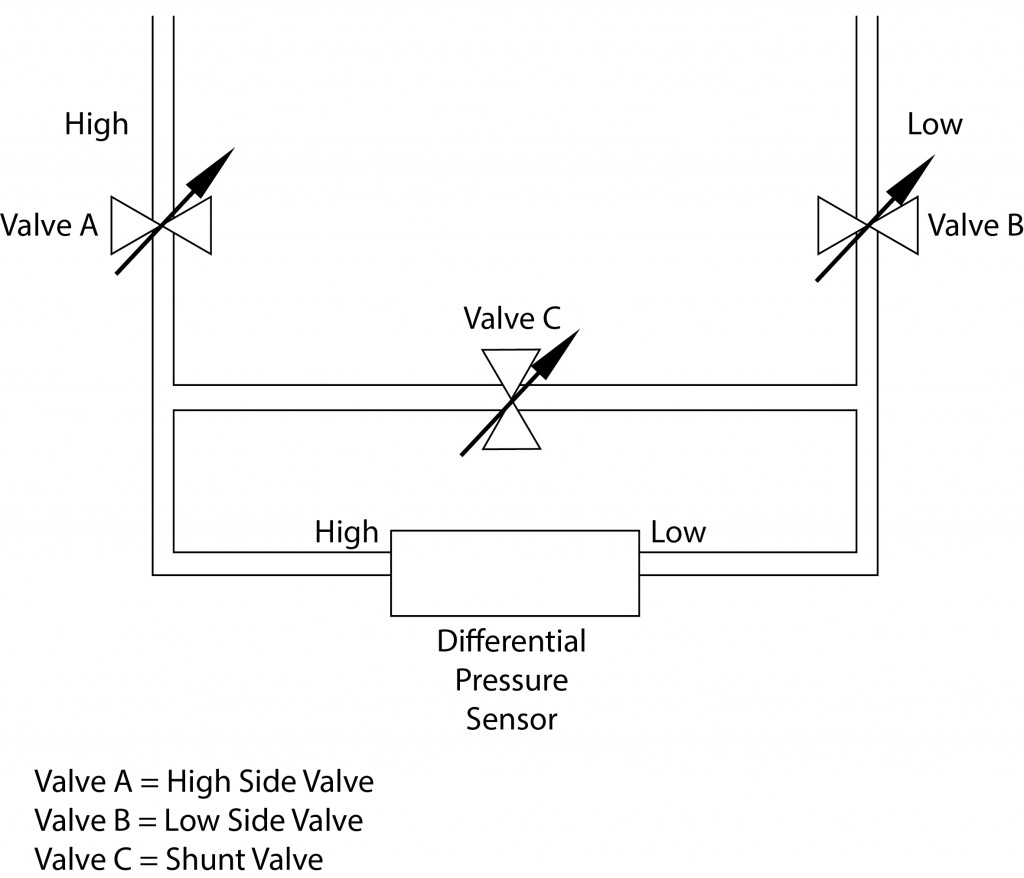
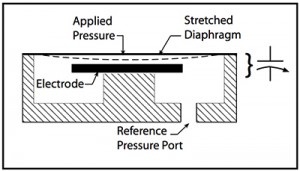
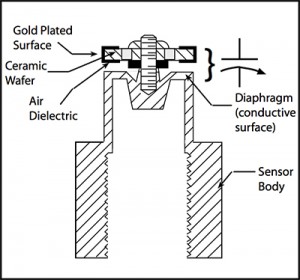
Low Pressure Measurement
Low pressure measurements are required in various applications such as air flow, static duct and clean room pressures in heating, ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) and energy management systems. Other applications include use in medical instrumentation, environmental pollution control, boiler combustion efficiency and a wide variety of research and development requirements. While this discussion will center mainly on air flows and pressures, the same principles also apply to liquids. As there are both pressure transducers (voltage output proportional to applied pressure) and pressure transmitters (current output proportional to applied pressure,) we will refer to each as pressure sensors in this application note.
Setra Blog
Capacitance based pressure transducers provide many benefits over other technologies. 8 features that should be considered when choosing a pressure transducer are accuracy, minimal mechanical motion, range capabilities, long term stability, high-level output, media compatibility, electromagnetic compatibility and resistant to harsh environments..
Often we hear terms used to describe pressure transducers or terms commonly used in the HVAC/R and industrial industries, but there may be some confusion as to their meaning. Here are a few commonly used terms and their definitions.
Equipment designers today can choose from an impressive array of commercially available pressure sensors.
Sensing devices range from modern versions of the venerable manometer and Bourdon tube, through bonded strain gauges to sophisticated units using, deposited or ion-implanted piezoresistive semiconductor elements on silicon or sapphire substrates.
Subscribe to Our Blog!
Topics
- Critical Environments (182)
- HVAC/R (179)
- General Industrial (153)
- Building Automation (134)
- General Industrial OEM (92)
- Energy Management (85)
- Test and Measurement (66)
- HVAC/R OEM (58)
- Barometric (44)
- Alternative Fuels (42)
- Medical (40)
- Process/Mfg Tank Level (40)
- Water and Wastewater (39)
- OHV (38)
- Oil and Gas (35)
- Industrial Vacuum (29)
- Calibration (25)
- Semiconductor (25)
- Particle Counting (20)
- Cleanroom Monitoring (17)
- Room Pressure Monitoring (16)
- Trade Show (12)
- cleanroom environment (12)
- Scales (11)
- Environmental Monitoring (10)
- Power Monitoring (10)
- Healthcare (9)
- Power Meters (9)
- Software (9)
- cleanroom monitoring systems (9)
- Case Study (8)
- critical environment technologies (8)
- data centers (8)
- Humidity (7)
- particle counter (6)
- pressure transducers (6)
- LITE room pressure monitor (5)
- hardware and software cleanroom monitoring systems (5)
- setra lite (5)
- Compliance (3)
- Video (3)
- hospital spaces (3)
- FAQ & Troubleshooting (2)
- Monitoring Compounding Pharmacies (2)
- Semiconductor Manufacturing (2)
- agencies that monitor pharmacies (2)
- energy (2)
- hvac (2)
- laboratories (2)
- monitor compound pharmacy (2)
- protected environment (2)
- regulatory compliance (2)
- setra lite features (2)
- usp 797 (2)
- Current Sensors and Transducers (1)
- Current Transformers (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery (1)
- Pressure (1)
- aerospace cleanrooms (1)
- cems (1)
- digital transformation (1)
- ipv6 multicast (1)
- ipv6 multicast address (1)
- ipv6 multicast address range (1)
- isolation room pressure monitoring (1)
- multicast address ipv6 (1)
- multicast ipv6 (1)
- operating room (1)
- pharma 4.0 (1)
- pressure sensor (1)
- pressure transducer companies (1)
- semi conductor (1)
- sensors and transducers (1)
- setra pressure transducers (1)
- submetering (1)
- sustainability (1)
- temperature monitor (1)
- temperature monitoring for pharmacies (1)
- transducers (1)
- usp 800 (1)
- water (1)
- what does hvac stand for (1)
- what is a transducer (1)
- what is hvac (1)