When first selecting a pressure transducer for a new project or piece of equipment, designers typically focus on key design parameters such as pressure range, electrical output, media compatibility and environmental conditions. However, those parameters are not the only ones to consider when making a smart choice for an application. There are three design considerations that are often overlooked when selecting a pressure transducer: transfer medium (oil filled vs. non-oil filled), construction, and type of sensing technology.
Setra Blog
Setra Systems will be exhibiting at the Automotive Testing Expo 2017 between October 24th and October 26th at the Suburban Collection Showplace in Novi, MI.
There are numerous environmental factors that can interfere with the performance of a pressure transducer. Two commonly overlooked factors are shock and vibration. Knowing the system where the pressure transducer is installed can help avoid high shock and vibration conditions, minimizing premature failure of your instrumentation.
Hysteresis Defined
According to Merriam-Webster, hysteresis is the “lagging of a physical effect on a body behind its cause (as behind changed forces and conditions)”. When outside forces act on an object, that object will either immediately spring back to its original state, or more likely, it will somehow change or exhibit properties from previous deformations.
Setra is best known for pioneering the variable capacitance principle, the technological innovation behind capacitance-based pressure transducers. Variable capacitance transducers demonstrate industry-leading accuracy especially in low pressure HVAC and critical care applications with accuracies as high as ±0.25” water column (±0.009 PSI).
As of July 22, the RoHS exemption for industrial monitoring and control instruments will end. Non- compliant product cannot be CE marked and sold in the European Union or to customers who otherwise require the CE mark.
Did you know that companies spend hundreds of millions of dollars on research and development for off-highway vehicle engines? A portion of the R&D goes into developing specialized engine test stands to ensure that the engines are functioning properly.
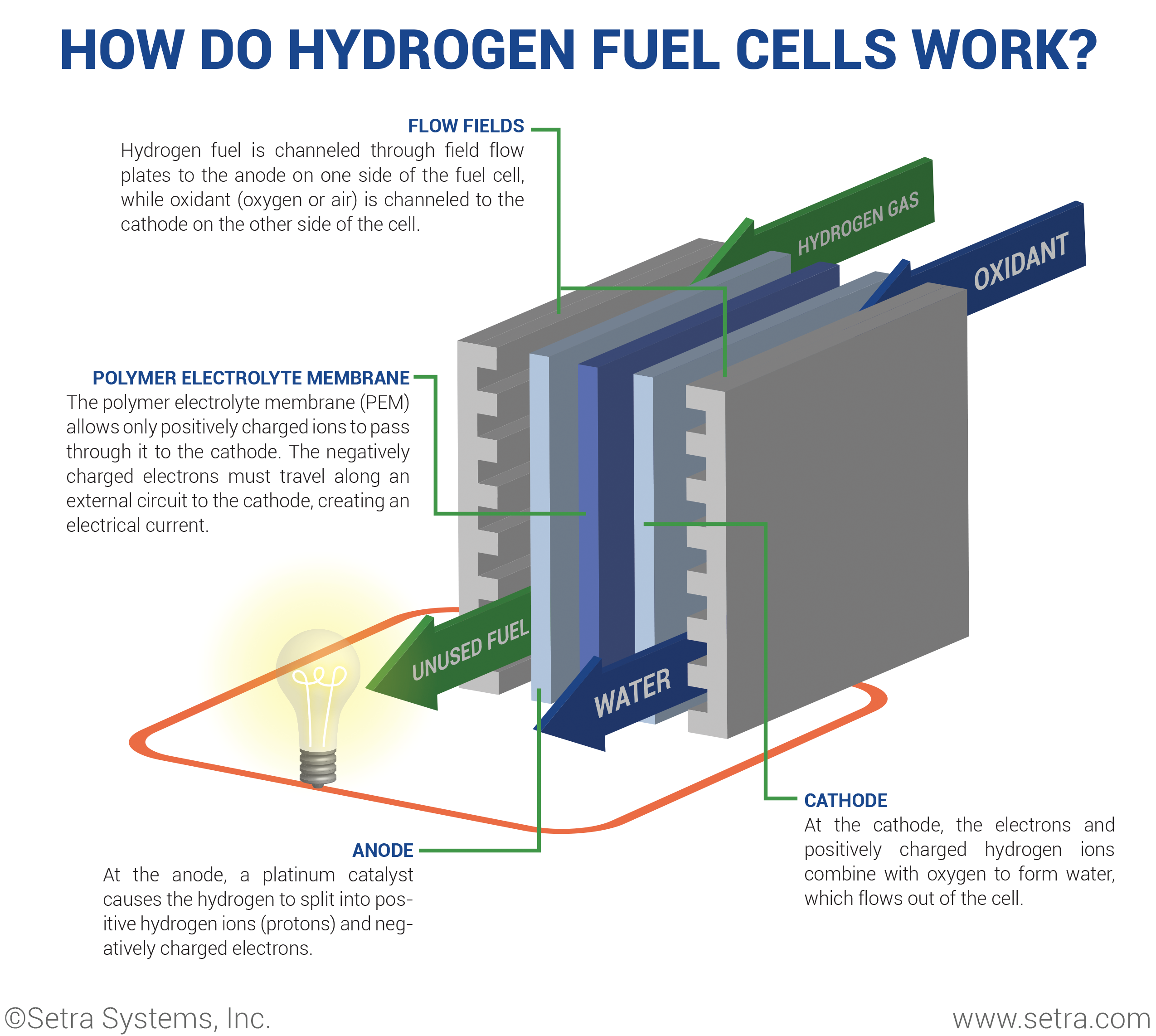
Engine test stands are complex, engineered systems designed to measure, control and record parameters during the different engine manufacturing stages.Although hydrogen is in its infancy as a fuel source, its future is incredibly bright. The technology behind hydrogen fuel cells is improving daily and its viability as a replacement to the internal combustion engine seems likely. Hydrogen is already being used in specialty vehicles such as forklifts and buses, and it’s only a matter of time before infrastructure is in place to serve the consumer automotive market. Why do hydrogen fuel cells have such great appeal? Because their only byproducts are heat and water vapor, making hydrogen fuel cells a truly zero-emission locomotive technology.
Capacitance is the ability of an object to hold an electrical charge. Capacitors are components in an electrical circuit that can store a charge and are considered one of the three fundamental electronic components along with inductors and resistors.
Simply put, barometric pressure is the measurement of air pressure in the atmosphere, specifically the measurement of the weight exerted by air molecules at a given point on Earth. Barometric pressure changes constantly and is always different depending on where the reading takes place.
Subscribe to Our Blog!
Topics
- Critical Environments (182)
- HVAC/R (179)
- General Industrial (153)
- Building Automation (134)
- General Industrial OEM (92)
- Energy Management (85)
- Test and Measurement (66)
- HVAC/R OEM (58)
- Barometric (44)
- Alternative Fuels (42)
- Medical (40)
- Process/Mfg Tank Level (40)
- Water and Wastewater (39)
- OHV (38)
- Oil and Gas (35)
- Industrial Vacuum (29)
- Calibration (25)
- Semiconductor (25)
- Particle Counting (18)
- Cleanroom Monitoring (17)
- Room Pressure Monitoring (16)
- Trade Show (12)
- cleanroom environment (12)
- Scales (11)
- Environmental Monitoring (10)
- Power Monitoring (10)
- Healthcare (9)
- Power Meters (9)
- Software (9)
- cleanroom monitoring systems (9)
- Case Study (8)
- critical environment technologies (8)
- Humidity (7)
- data centers (7)
- particle counter (6)
- pressure transducers (6)
- LITE room pressure monitor (5)
- hardware and software cleanroom monitoring systems (5)
- setra lite (5)
- Compliance (3)
- Video (3)
- hospital spaces (3)
- FAQ & Troubleshooting (2)
- Monitoring Compounding Pharmacies (2)
- Semiconductor Manufacturing (2)
- agencies that monitor pharmacies (2)
- energy (2)
- hvac (2)
- laboratories (2)
- monitor compound pharmacy (2)
- protected environment (2)
- regulatory compliance (2)
- setra lite features (2)
- usp 797 (2)
- Current Sensors and Transducers (1)
- Current Transformers (1)
- Pressure (1)
- aerospace cleanrooms (1)
- cems (1)
- digital transformation (1)
- ipv6 multicast (1)
- ipv6 multicast address (1)
- ipv6 multicast address range (1)
- isolation room pressure monitoring (1)
- multicast address ipv6 (1)
- multicast ipv6 (1)
- operating room (1)
- pharma 4.0 (1)
- pressure sensor (1)
- pressure transducer companies (1)
- semi conductor (1)
- sensors and transducers (1)
- setra pressure transducers (1)
- submetering (1)
- sustainability (1)
- temperature monitor (1)
- temperature monitoring for pharmacies (1)
- transducers (1)
- usp 800 (1)
- water (1)
- what does hvac stand for (1)
- what is a transducer (1)
- what is hvac (1)