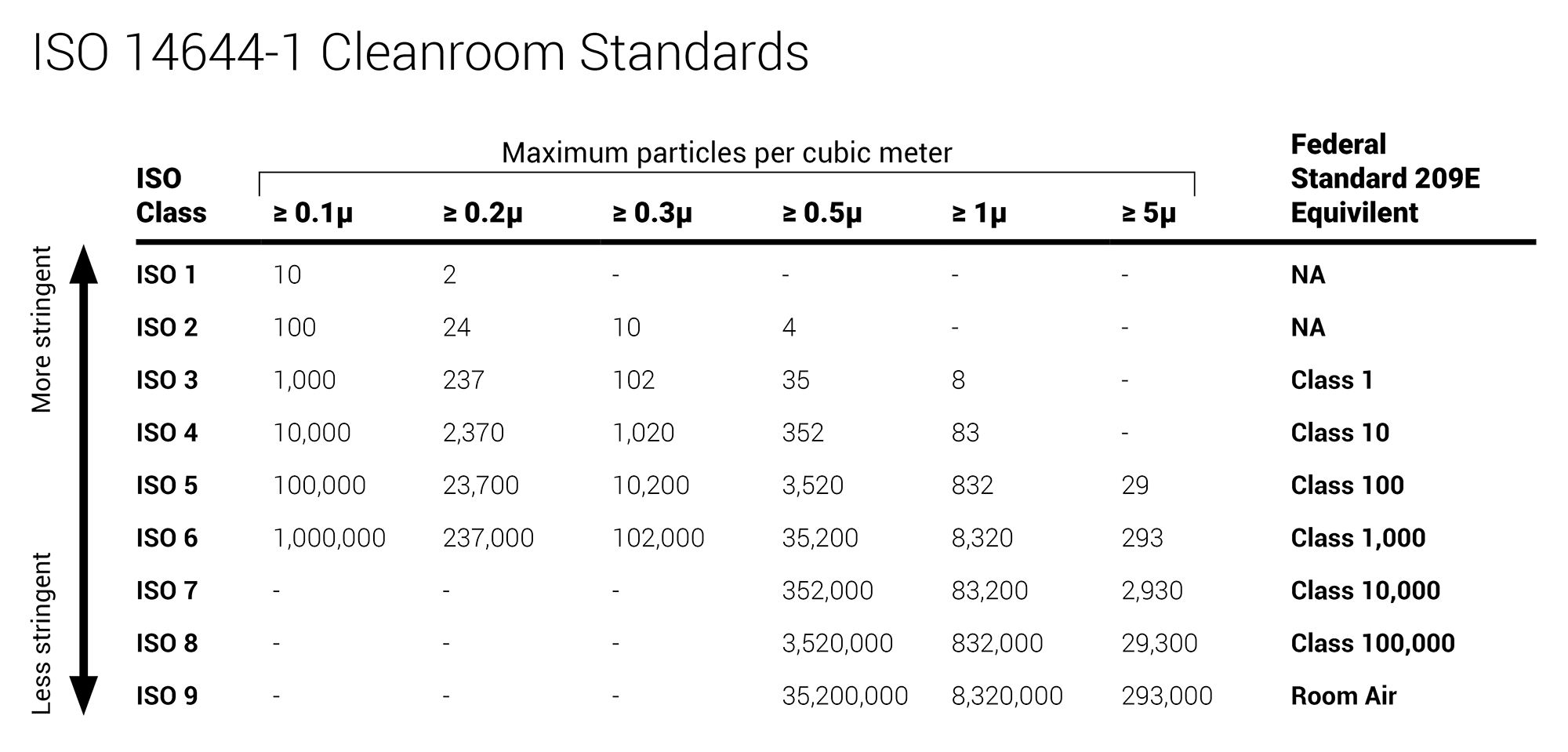
OEM and mechanical parts suppliers adopting ISO Standards is increasingly common throughout the US, driven by a spike in industry demand for components manufactured in ISO compliant factories. In addition to existing and increasing demand for ISO compliance in clean rooms, healthcare spaces, and laboratories, manufacturing facilities like automotive, electronics, loT, and industrial are now adapting to observe these standards. To be ISO compliant, all of these spaces need highly accurate, reliable, and NIST-traceable sensors for monitoring.
Setra Blog
When selecting a particle counter, it is necessary to consider what building automation network it can communicate with. Examining the available options helps to ensure the particle counter will connect to your existing network.
Nosocomial infections (also known as Hospital-Acquired Infections, Healthcare-Associated Infections, or HAIs) can result in otherwise avoidable extended hospital stays, readmittance, follow-up treatments, and even death. HAIs can often spread via airborne transmission, which emphasizes the need for proper room pressurization to contain hazardous particles. Operating rooms (ORs) are an area where patients are especially at risk for contracting infections. 2.5µm particles are an important leading indicator of the potential presence of contaminants that could put the patient at risk. The best opportunity to manage the risk of infections is by limiting 2.5µm particles in a space.
Inhaling airborne particles can put both critical patients and healthcare staff at risk for detrimental health issues. Controlling these particles is necessary for protecting both staff and occupants of nearby rooms from exposure to infectious particles. To maintain safety in a hospital, it is crucial to monitor both differential pressure and particle counts in anterooms.
Requirements and regulations are becoming ever more stringent for critical environments, making finding the right products for a space increasingly difficult. Not only must the specs of the product be considered, but the supplier must be taken into account as well. Shopping around with the intent to purchase from a variety of vendors takes a significant amount of time and effort. In addition to wasted time and effort, buying from multiple vendors comes associated with a number of risks and drawbacks, including:
- Incompatible hardware
- Incompatible software
- Minimal or disjointed tech support
- Inability to integrate products
- Installation and operational issues
1. Recognize the difference between BACnet options
BACnet has a multitude of protocols available, but Setra products typically only operate on one of two options.
Twice a year, many critical environments - such as compounding pharmacies and cleanrooms - undergo particle certification. To obtain room certification, either a minimum sample volume (as written in the EC GMP Annex 1) should be taken, or the sequential sampling technique (as identified in both FS209E and ISO 14644-1) should be used. However, since this particle certification usually occurs only every six months, many critical environments are unaware of their particle counts during the remainder of the year.
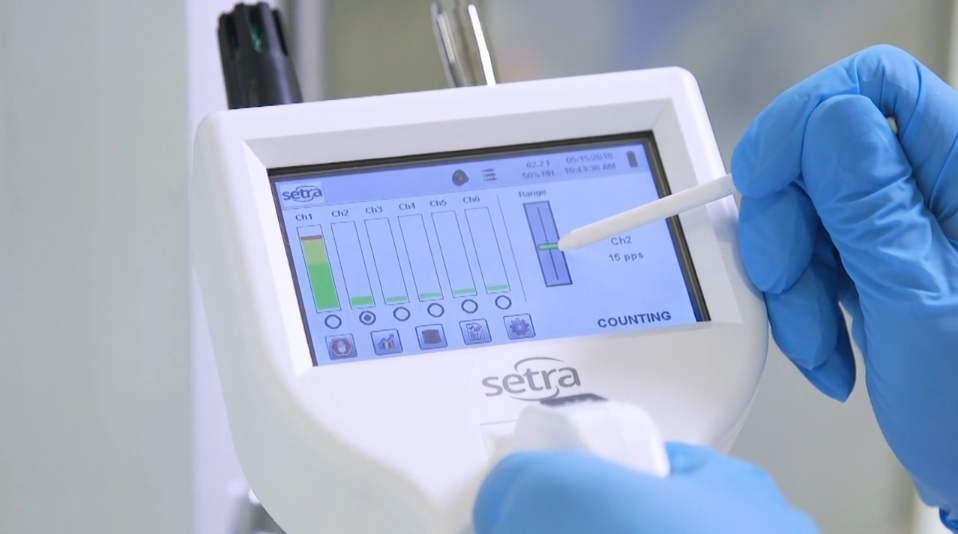
Flow rate is important to consider when selecting a particle counter for a critical environment. The flow rate of a particle counter is the rate at which a pump draws air through the sample chamber, measured in cubic feet per minute (cfm). Two common flow rates for particle counters are 1 cfm and 0.1 cfm. Depending on the application, each flow rate can be valuable.
In most hospital pharmacy cleanrooms, standard operating procedure includes sampling of air quality for viable particles (i.e. particles that include or are composed of microorganisms). These tasks are traditionally executed with an air sampler containing agar strips or simply by placing agar contact plates on surfaces throughout the facility. These samples are then left to incubate and are then analyzed to determine the environment’s air quality.
Hospital pharmacies are unique because of the critical role they play in maintaining patient health and safety. Pharmacies that perform compounded sterile preparations (CSPs), in particular, must meet specific clean room standards to ensure sterile conditions are maintained. While there are many established environmental requirements in these spaces, some pharmacy managers are choosing to go the extra mile in exchange for added peace of mind.
Subscribe to Our Blog!
Topics
- Critical Environments (182)
- HVAC/R (179)
- General Industrial (153)
- Building Automation (134)
- General Industrial OEM (92)
- Energy Management (85)
- Test and Measurement (66)
- HVAC/R OEM (58)
- Barometric (44)
- Alternative Fuels (42)
- Medical (40)
- Process/Mfg Tank Level (40)
- Water and Wastewater (39)
- OHV (38)
- Oil and Gas (35)
- Industrial Vacuum (29)
- Calibration (25)
- Semiconductor (25)
- Particle Counting (20)
- Cleanroom Monitoring (17)
- Room Pressure Monitoring (16)
- Trade Show (12)
- cleanroom environment (12)
- Scales (11)
- Environmental Monitoring (10)
- Power Monitoring (10)
- Healthcare (9)
- Power Meters (9)
- Software (9)
- cleanroom monitoring systems (9)
- Case Study (8)
- critical environment technologies (8)
- data centers (8)
- Humidity (7)
- particle counter (6)
- pressure transducers (6)
- LITE room pressure monitor (5)
- hardware and software cleanroom monitoring systems (5)
- setra lite (5)
- Compliance (3)
- Video (3)
- hospital spaces (3)
- FAQ & Troubleshooting (2)
- Monitoring Compounding Pharmacies (2)
- Semiconductor Manufacturing (2)
- agencies that monitor pharmacies (2)
- energy (2)
- hvac (2)
- laboratories (2)
- monitor compound pharmacy (2)
- protected environment (2)
- regulatory compliance (2)
- setra lite features (2)
- usp 797 (2)
- Current Sensors and Transducers (1)
- Current Transformers (1)
- Lithium-Ion Battery (1)
- Pressure (1)
- aerospace cleanrooms (1)
- cems (1)
- digital transformation (1)
- ipv6 multicast (1)
- ipv6 multicast address (1)
- ipv6 multicast address range (1)
- isolation room pressure monitoring (1)
- multicast address ipv6 (1)
- multicast ipv6 (1)
- operating room (1)
- pharma 4.0 (1)
- pressure sensor (1)
- pressure transducer companies (1)
- semi conductor (1)
- sensors and transducers (1)
- setra pressure transducers (1)
- submetering (1)
- sustainability (1)
- temperature monitor (1)
- temperature monitoring for pharmacies (1)
- transducers (1)
- usp 800 (1)
- water (1)
- what does hvac stand for (1)
- what is a transducer (1)
- what is hvac (1)