Absolute pressure is measured relative to a full vacuum (0 PSIA = 14.7 PSIV). The electrical output of an absolute pressure transducer is 0 VDC at 0 PSIA and full scale output (typically 5 VDC) at full scale pressure (in PSIA). PSIA (pounds per square inch absolute) is a unit of pressure measured relative to a full vacuum. A vacuum can refer to any pressure between 0 PSIA and 14.7 PSIA.
An absolute pressure transducer gives an increased positive voltage output proportional to increasing pressure (above full vacuum. In this example, we'll see how a vacuum transducer and an absolute transducer compare with pressure ranges and output. (See Figure 1 and 2)
Figure 1:
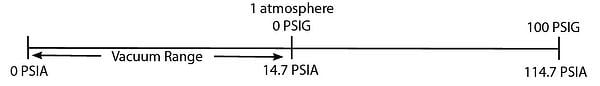
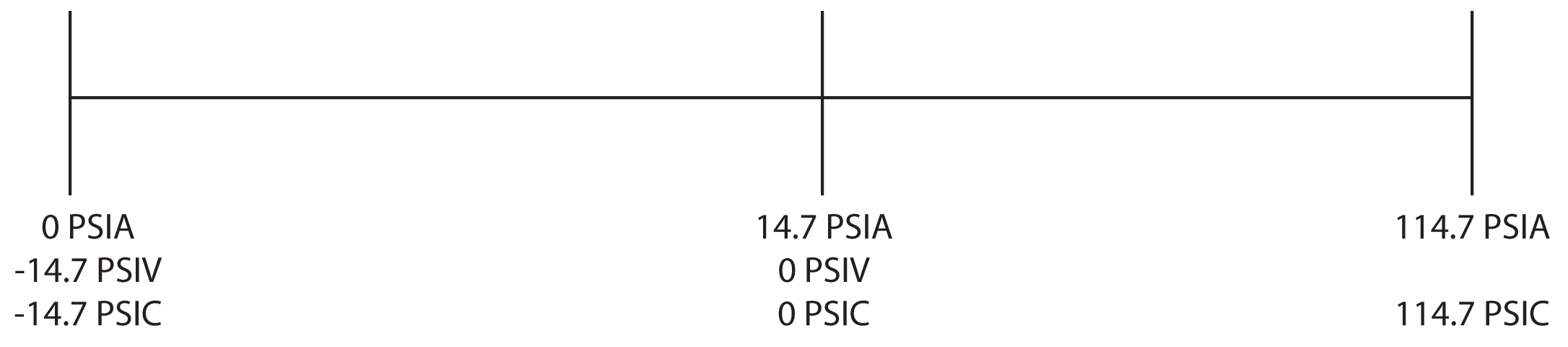
Figure 2:

Vacuum Transducer
- Range: 0 to 14.7 PSIV
- Output: 0 to 5vDC
Absolute Transducer
- Range: 0 to 14.7 PSIA
- Output: 0 to 5 VDC
Applications that require measuring pressures below atmosphere to pressure above atmosphere, regardless of the barometric pressure of the day or altitude of the location, utilize absolute pressure ranges to get the same result.
Applications that require measuring pressures below atmosphere to pressure above atmosphere utilizing compound pressure ranges, will have varying results based on the barometric pressure of the day or altitude of the location. This is due to the fact that the 0 is referencing a full vacuum. (See Figure 3).
CLICK HERE to better understand the difference between PSI, PSIA and PSIG.


